Can a Fish Survive With a Hook in Its Mouth
A fish can sometimes survive with a hook in its mouth, although it may face health challenges. The survival chances depend on the hook’s location and whether it causes significant damage.
Fishing is a popular pastime, yet many don’t consider the survival odds of fish after catch-and-release. Can these creatures live on with a piece of metal lodged in their mouths? It’s a question of resilience and the robust healing processes fish possess.
A hook in the lip, for example, can be less life-threatening than one in the gill or gut, which can lead to serious injury or death. Anglers often wonder about the fate of fish post-release. Understanding the factors that affect a fish’s chances can improve practice for those who indulge in this sport while promoting aquatic welfare. Survival is indeed a possibility, but it’s not guaranteed—fish health can be compromised, affecting their ability to eat, evade predators, or avoid infection.
Credit: www.quora.com
The Plight Of Hooked Fish
Fish can suffer greatly with hooks left in their mouths. The impact of fishing hooks on a fish’s survival can vary. Small, smooth hooks may cause less damage and improve chances of survival. Yet, large or barbed hooks can lead to severe injury and lower the survival rate.
Some fish can live with hooks if they don’t disrupt eating or cause infection. Hooks in less vital areas might be shed or absorbed over time. Fish struggle to survive with hooks that damage vital organs. Proper catch and release techniques matter for fish health. Anglers can aid survival by using environmentally-friendly hooks and proper unhooking methods.
Fish Anatomy And Hook Hazards
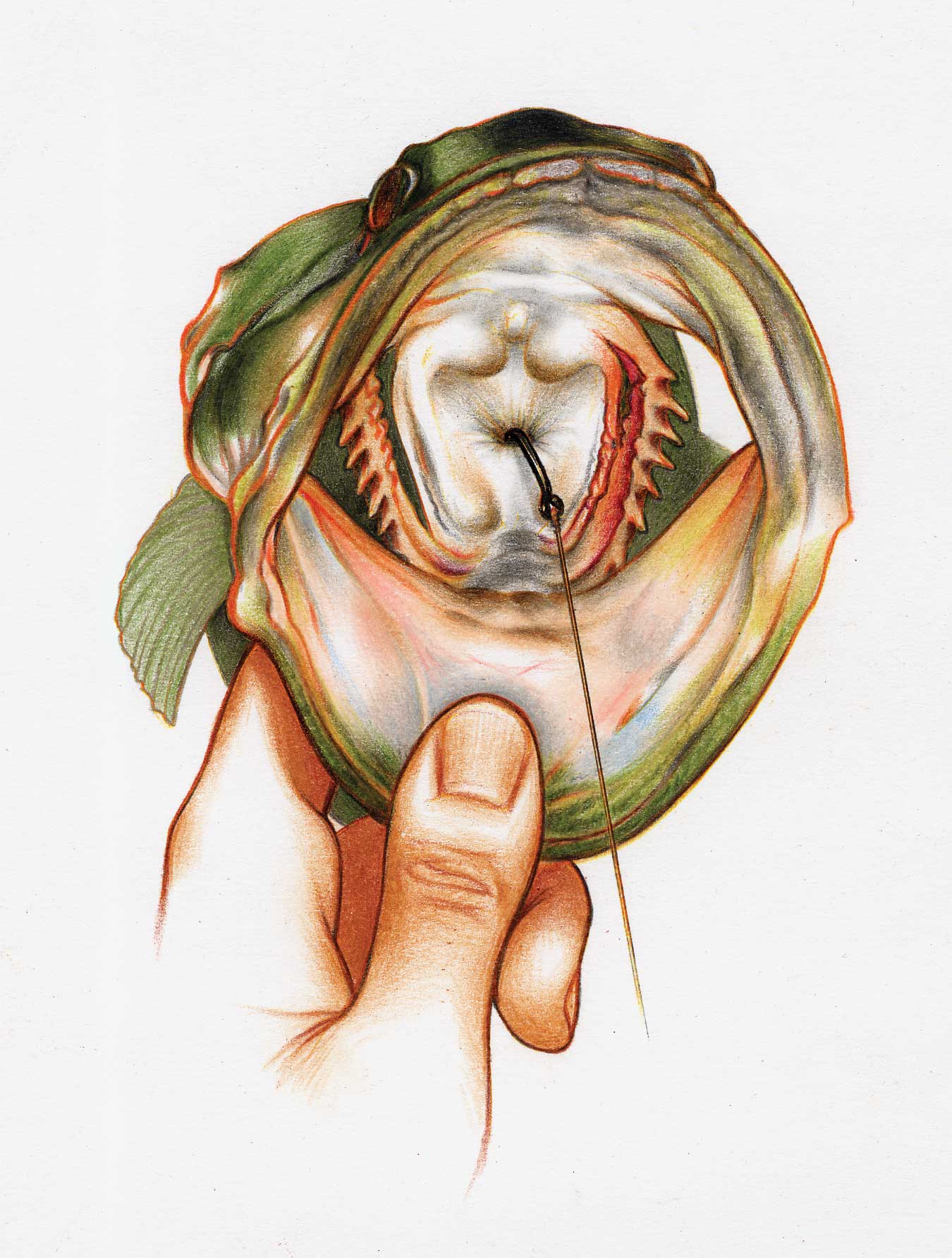
The mouth of a fish is unique and vital for its survival. It uses its mouth to eat, breathe, and sometimes even move. A hook can cause serious harm to these functions. The inner mouth structure is delicate. Bones, blood vessels, and nerves are at risk of damage from a hook.
Sharp hooks can cut or pierce through this sensitive area. This leads to pain and can prevent the fish from eating properly. The likelihood of infection increases with an injury. Also, a hook left in a fish’s mouth may rust. Rust can release harmful substances, putting the fish’s health at risk.
Factors Affecting Hook Survival
The size of the hook plays a key role in a fish’s survival. Smaller hooks may cause less damage and are often easier to dislodge. The material of the hook also factors in. Stainless steel hooks are harder to corrode. This means they stay in the fish longer than hooks made from other materials.
The location of the hook in the fish’s mouth is critical. If the hook is in the lip or jaw, the fish may live longer. A hook stuck in the throat can cause more harm and affect the fish’s eating.
Different fish species have varying abilities to heal and adapt. Some species can survive well with a hook. Others may struggle to survive.
Healing Process In Fish
Fish have amazing natural healing abilities. A small hook wound often heals by itself. Their bodies can close a wound within just a few days. Immune systems in fish work hard to fix them. White blood cells fight off any germs that come in. This keeps the fish healthy. Even with hooks, fish can heal and survive. This shows how tough fish are.
The Role Of Anglers
Catch and release practices are vital for fish survival after angling. Anglers play a critical role in ensuring the health of fish populations. Proper handling techniques and quick releases reduce stress and injury to fish.
Using barbless hooks and rubberized nets can significantly decrease the damage done during capture. It’s essential to keep the fish in the water while removing the hook. Wet hands or gloves can prevent removal of the fish’s protective slime coat.
Avoid touching the gills or eyes. Fish should be supported horizontally when held out of water. Revive the fish until it swims away strongly on its own. Education about ethical angling is key for the sustainability of the sport.
Credit: www.in-fisherman.com
Research And Conservation Efforts
Recent studies on hook injury highlight fish resilience. Certain fish can heal after hook injuries. Survival rates vary by species, hook type, and injury location. Mortality rates decrease with prompt hook removal. Catch-and-release practices contribute to fish conservation.
Advancements in fishing gear aim for sustainability and reduced harm. Barbless hooks and circle hooks cause fewer injuries. Researchers encourage using safer gear. Anglers become aware, thanks to conservation programs.
| Hook Type | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Barbless Hooks | Easy removal, less damage |
| Circle Hooks | Hook fish in the mouth, avoiding gut hooks |

Credit: www.saltstrong.com
Frequently Asked Questions For Can A Fish Survive With A Hook In Its Mouth
How Long Does A Hook Last In A Fish’s Mouth?
A hook can remain in a fish’s mouth for several weeks to months before dissolving or falling out, depending on the material.
Do Fish Survive After Being Hooked?
Many fish can survive after being hooked and released, especially if handled properly and returned quickly to the water. Survival rates vary by species and circumstances.
Does A Hook Hurt A Fishes Mouth?
Yes, a hook can cause pain and injury to a fish’s mouth, which is sensitive and can hurt, like human mouths.
Do Fishes Mouths Heal After Being Hooked?
Fish mouths can heal after being hooked, but the healing speed varies based on the fish species and the injury’s severity. Proper catch-and-release techniques improve healing chances.
Conclusion
Understanding fish health and safety is crucial for responsible fishing. Though some fish can endure with a hook in their mouth, risks remain high. Prompt hook removal and proper catch-and-release techniques are essential. Protect our aquatic friends and ensure their survival for future generations.
Remember, every hook counts.