What Does It Mean When a Lake Turns Over

When a lake turns over, it refers to the process of the rapid mixing of lake water due to rapid changes in weather temperatures. This phenomenon can have devastating effects on fish, plants, and amphibians that live in the lake.
It occurs during seasonal changes when the water begins to warm up or cool down, which stirs up bottom sediments and creates anaerobic conditions. This, in turn, releases mass quantities of sulfur and methane gases into the atmosphere. The duration of lake turnover varies with each lake and its location, but it typically takes a few weeks for the process to occur.
Understanding Lake Turnover
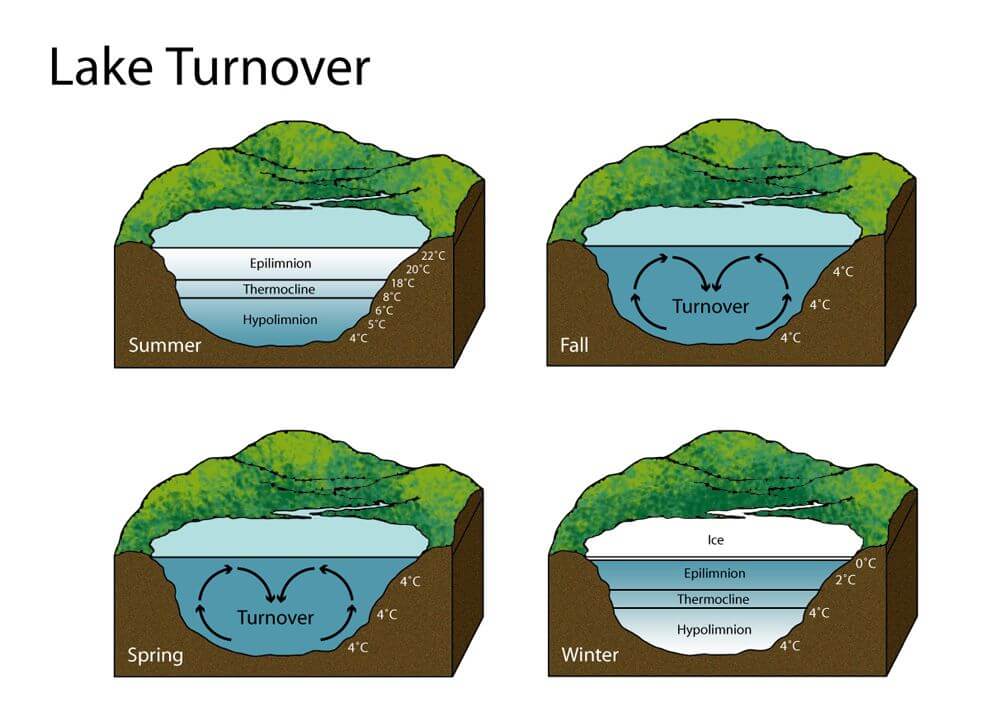
When a lake turns over, it means that there is an exchange of water between the surface and bottom layers. This process is crucial for maintaining the overall health and balance of the lake ecosystem. During the summer, the lake becomes stratified with warmer, lighter water on top and cooler, denser water at the bottom. This stratification creates distinct layers that house different organisms. When fall arrives, the cooling weather causes the lake to undergo a turnover where the surface and bottom waters mix, bringing oxygen-rich water to the depths and nutrients to the surface. This natural phenomenon impacts the distribution and availability of food for fish and other aquatic life, influencing fishing patterns and the health of the lake.
Credit: www.cleanlakesalliance.org
Effects Of Lake Turnover
When a lake undergoes turnover, it can have various effects on the ecosystem, including the fish population and fishing opportunities. During turnover, which is a natural process that occurs due to changes in weather temperatures, the lake water rapidly mixes. This mixing can be detrimental to fish, plants, and amphibians that reside in the lake. The sudden changes in temperature and oxygen levels can disrupt the habitat and potentially cause fish mortality.
For fishermen, lake turnover can have both positive and negative effects. Some anglers believe that trout fishing improves after turnover because the cooler water conditions attract the fish to the surface. However, overall fishing can be challenging during this period due to the disruption in the ecosystem. It may take some time for the fish to adjust to the changing conditions.
It is important to note that the duration of lake turnover can vary. In general, the turnover process occurs during the spring and fall when the water temperatures change. The length of turnover can range from a few weeks to longer, depending on the specific lake and its geographical location.
Duration Of Lake Turnover
During lake turnover, the water in a lake mixes and this process can have significant effects on the lake ecosystem. The duration of lake turnover can vary depending on factors such as the size of the lake and the weather conditions. In general, the turnover process usually takes a few weeks. However, it is important to note that this timeframe can vary from lake to lake. Lake turnover typically occurs during the spring and fall when the water temperatures change. It is during these periods that the surface waters cool and become denser, causing them to sink and mix with the deeper waters. This mixing helps to distribute nutrients and oxygen throughout the lake, which is important for the survival of aquatic organisms. Lake turnover also plays a role in releasing gases such as sulfur and methane into the atmosphere.
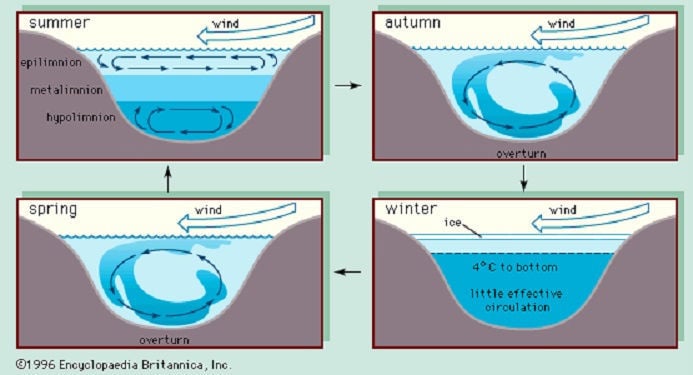
Credit: beatricedailysun.com
Impacts Of Lake Turnover On The Ecosystem
Lake turnover is a natural phenomenon that can have devastating effects on fish, plants, and amphibians living in the lake. During rapid changes in weather temperatures, the rapid mixing of lake water occurs. Cooler weather causes the lake or pond to turn over, stirring bottom sediments and mixing anaerobic conditions throughout the entire pond, releasing mass quantities of sulfur and methane gases into the atmosphere. This process can negatively impact the ecosystem, altering the ecosystem’s balance and biological diversity. As such, it is crucial to understand the implications of lake turnover on aquatic life and take measures to mitigate its potential harmful effects.
Benefits Of Lake Turnover
When a lake turns over, it brings various benefits to the ecosystem. One of the advantages is cleaning up harmful bacteria and algae. During turnover, the water column mixes, causing oxygen-rich surface water to mix with the oxygen-depleted bottom water. This process helps to distribute oxygen throughout the lake, which is essential for the survival of aquatic organisms. By increasing oxygen levels, turnover can help control the growth of harmful bacteria and algae, promoting a healthier ecosystem. Additionally, turnover can also facilitate the cycling of nutrients, ensuring that essential elements are available to support the growth of aquatic plants and animals. Overall, lake turnover plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance and health of the lake’s ecosystem.
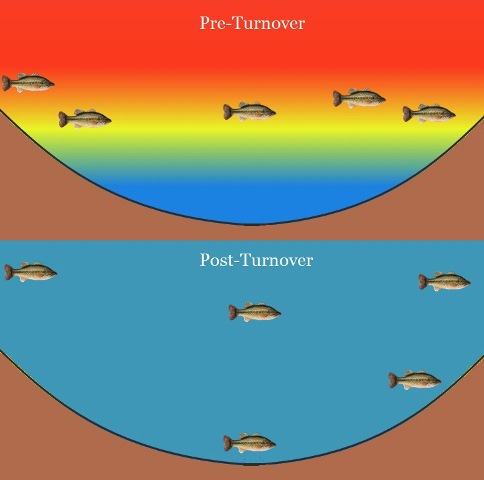
Credit: blog.fishidy.com
Frequently Asked Questions For What Does It Mean When A Lake Turns Over
What Happens To Fishing When A Lake Turns Over?
During a lake turnover, the mixing of lake water can have effects on fish and fishing. Trout fishing tends to improve after a turnover because the water becomes cooler. The turnover process usually takes a few weeks and varies depending on the lake and location.
How Long Does It Take A Lake To Turn Over?
A lake typically takes a few weeks to turn over, but the duration varies depending on its location and conditions. Turnover occurs during rapid weather temperature changes, resulting in a rapid mixing of lake water. This natural phenomenon can have significant effects on the lake’s ecosystem.
What Happens When A Lake Overturns?
When a lake overturns, the water undergoes rapid mixing, resulting in changes in temperature and oxygen levels. This can have negative effects on the fish, plants, and amphibians living in the lake. Turnover is a natural phenomenon caused by rapid changes in weather temperatures.
What Happens When A Lake Or Pond Turns Over?
During lake or pond turnover, the water mixes, causing the bottom sediments to stir and releasing sulfur and methane gases. This process can have negative effects on fish, plants, and amphibians living in the water. Turnover is a natural phenomenon that occurs during rapid changes in weather temperatures.
Conclusion
Understanding the process of a lake turnover is vital for both the ecosystem and recreational activities. The mixing of water layers influences the distribution of nutrients and affects the aquatic life. By knowing the implications of lake turnover, we can better appreciate and manage the health of our lakes.